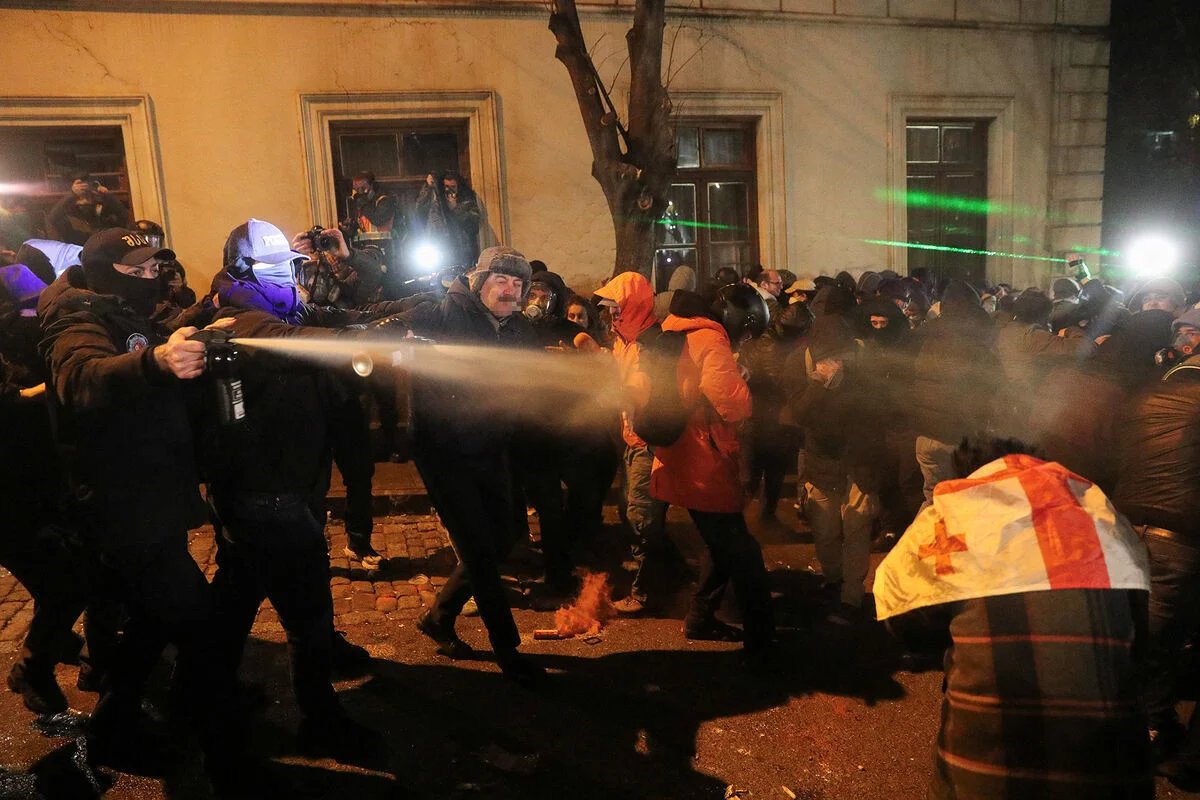The recent events in Georgia have caused significant concern in the European Union. The Georgian government’s refusal to pursue European integration and the protests in Tbilisi are forcing the EU to consider potential pressure measures, including sanctions and visa restrictions.
EU Response
EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs Josep Borrell stated that the EU condemns the use of force against demonstrators and notes alarming signs of democracy backsliding in the country. He emphasized that the actions of the Georgian government will have “direct consequences.” One of the sanction options being discussed by EU countries is limiting visa liberalization for Georgian citizens.
Such statements come amid escalating domestic political crisis in the country. Several Georgian ambassadors in Europe have already announced their resignations in protest against the decision of the ruling party “Georgian Dream” to freeze EU accession talks until 2028.
Political Crisis and Georgia’s Position
In response to the actions of the Georgian government, the opposition and pro-European forces in the country are calling for new parliamentary elections. Zurabishvili, the President of Georgia, stated that the current parliament does not have the right to elect a new president, and her term will continue until the completion of the electoral process by the new parliament.
These statements have only fueled the protests that have engulfed the capital and major cities. Demonstrators are demanding a return to the European course and an immediate halt to the “democratic backtracking” policy.
Possible Consequences for Georgia
Georgia’s decision to temporarily suspend the process of Eurointegration may have far-reaching consequences. Firstly, it risks depriving the country of access to important support programs from the EU. Secondly, Georgia’s international reputation as a country aspiring to European values could be seriously undermined.
European policymakers emphasize that deviating from Eurointegration jeopardizes the country’s economic and social future, particularly its relations with key European partners.
Looking to the Future
Protests in Tbilisi indicate a divide within Georgian society. Citizens seek change and see their future in the EU, while the government opts for a more isolated policy. Experts note that the crisis can only be resolved through new elections and a return to democratic values.
Can Georgia regain its path towards European development? It depends on the decisions of the country’s leadership and the pressure from the international community. The EU, in turn, is ready to support Georgia, but only on the condition of restoring the course of reforms and Eurointegration.